
Back Operculum (Gehirn) German درپوش (مغز) Persian Operculum (aivot) Finnish Opercolo (cervello) Italian Operculum (cerebrum) Latin Wieczko (anatomia) Polish 岛盖 Chinese
| Operculum (brain) | |
|---|---|
 Operculum | |
 Parietal operculum (green), temporal operculum (blue), and insular cortex (brown), with red inset showing the position of the brain slice. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | operculum frontale, operculum parietale, operculum temporale |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |

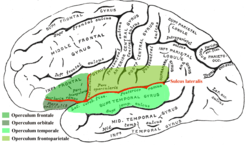
In human brain anatomy, an operculum (Latin, meaning "little lid") (pl.: opercula), may refer to the frontal, temporal, or parietal operculum, which together cover the insula as the opercula of insula.[1] It can also refer to the occipital operculum, part of the occipital lobe.
The insular lobe is a portion of the cerebral cortex that has invaginated to lie deep within the lateral sulcus. It sits like an island (the meaning of insular) almost surrounded by the groove of the circular sulcus and covered over and obscured by the insular opercula.
A part of the parietal lobe, the frontoparietal operculum, covers the upper part of the insular lobe from the front to the back.[2] The opercula lie on the precentral and postcentral gyri (on either side of the central sulcus).[3] The part of the parietal operculum that forms the ceiling of the lateral sulcus functions as the secondary somatosensory cortex.
- ^ Dorland 2012, p. 1328
- ^ Dorland 2012, p. 1327
- ^ Joseph M. Tonkonogy; Antonio E. Puente (23 January 2009). Localization of Clinical Syndromes in Neuropsychology and Neuroscience. Springer Publishing Company. p. 392. ISBN 978-0-8261-1967-4. Retrieved 12 October 2012.